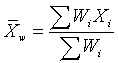
StATS: What is a weighted mean?
The weighted mean is a mean where there is some variation in the relative contribution of individual data values to the mean. Each data value (Xi) has a weight assigned to it (Wi). Data values with larger weights contribute more to the weighted mean and data values with smaller weights contribute less to the weighted mean. The formula is
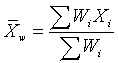
There are several reasons why you might want to use a weighted mean.
Further reading
This page was written by Steve Simon while working at Children's Mercy Hospital. Although I do not hold the copyright for this material, I am reproducing it here as a service, as it is no longer available on the Children's Mercy Hospital website. Need more information? I have a page with general help resources. You can also browse for pages similar to this one at Category: Definitions, Category: Definitions, Category: Descriptive statistics.